HTML
-
精密光束指向(fine pointer of beam, FPB)系统又称快速反射镜, 是在较小的机械转角范围内(小于5°), 可精密控制指向的光机系统。其具有响应速度快、指向精度高、伺服带宽高等优点, 已经广泛地应用于稳像、稳瞄、主动光电对抗等军事领域, 并成为该类系统的核心组件[1-7]。FPB对控制系统的响应速度及控制精度均有较高要求, 采用传统比例-微分-积分(proportional-integration-differential, PID)控制器不能很好地解决系统快速性和超调量的矛盾。为了获得更高的性能指标和良好的控制效果, 国内外学者对此进行大量研究:DAI等人提出了一种快速抑制超调量的改进预测控制算法, 在提高动态响应的同时, 减少了超调量[8]; HUANG等人提出反馈微分和前馈微分自适应控制的新型控制策略, 解决了位置伺服系统响应超调性和快速性之间的矛盾[9]; LONG等人提出基于退火算法提出一种全局优化的PID控制算法, 提升了低频跟随及高频振动抑制能力[10]; TANG等人[11]在PID控制器基础上额外增加一个积分环节, 从而减小了快反镜系统低频误差; NESTOR等人提出一种基于自适应网格滤波器的可变阶数自适应控制器, 并应用于微机电结构快速反射镜中, 有效地扩展了抗扰动带宽范围; NESTOR等人[12]研究基于前馈及自适应滤波的快反镜控制器, 提升了系统的响应范围及速度, 从而对振动及光学抖动等的补偿具有更好的效果。由上述内容可知, 目前国外高性能FPB的控制系统研究已经转向模糊控制、神经网络、自适应控制等为实现手段的现代控制理论领域, 并取得了优于传统控制理论的结果。但在实际工程应用中, FPB系统的计算能力始终受到成本及使用环境等外界条件的限制, 从而使新型控制器的应用受到一定的制约; 因此, 如何立足现有FPB控制系统硬件平台实现更高的控制性能是目前迫切需求。
本文中在对传统控制算法研究分析的基础上, 设计了复合PID算法, 用于解决系统快速性和超调量之间的矛盾, 且该算法的计算量及实时性可满足计算能力受限制的精密光束指向系统的要求。最后通过对比试验, 证明本文中所研制控制器的性能优于传统PID控制器。
-
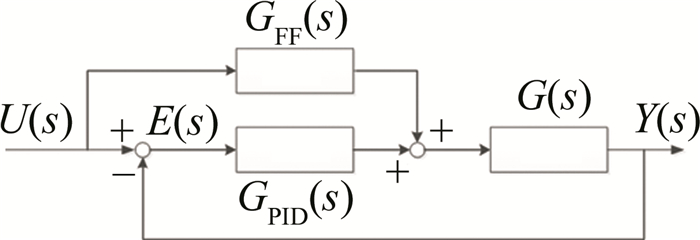
前馈控制在高精度伺服系统中常用于提高系统的快速性。但由于其为开环控制, 在受负荷和工况等的影响时, 无法检验自身补偿的效果, 因此控制精度不高。而反馈调节则能够消除扰动给系统带来的影响, 具有较高的控制精度高[13-14]。因此前馈补偿PID将两者优点相结合, 能够在提高系统快速性的同时, 提高系统控制精度。前馈补偿PID控制器的结构如图 1所示。
图 1中, U(s)为系统输入信号, E(s)为系统误差信号, GFF(s)为前馈补偿算法传递函数, GPID(s)为PID控制器传递函数, G(s)为系统的开环传递函数。则前馈补偿PID系统的传递函数可由下式表示:
对(1)式进行整理, 则系统误差E(s)对输入U(s)的传递函数可由下式表示:
从(2)式可以看出, 当1-GPID(s)G(s)=0, 即GFF(s)=1/G(s)时, 可使得系统的误差为零。在实际的系统中, 系统误差虽无法完全消除, 但可以将其降低至可接受的范围, 从而在获得更好动态特性的前提下, 仍具有较高的控制精度。
-
高性能FPB系统由于对调节时间及稳态误差有更高的要求, 因此出现多种新型控制器结构及实现方式[15-21], 但其复杂程度与计算量和传统PID调节器相比大大增加。该系统为了满足较宽的工作温度而采用工业级的数字信号处理器(digital signal processor, DSP)作为主控芯片, 并降频30%使用。其运算能力与目前市面主流商业级DSP相比较为有限。因此直接采用算法复杂程度较高的控制器时, 实时性难以保证。为此本文中设计了基于前馈补偿PID算法及抗积分饱和算法的复合PID控制器, 在算法复杂程度及计算实时性不显著增加前提下, 有效的FPB减小调节时间及稳态误差。其结构如图 2所示。
图 2中, u(k)为被控对象期望值(即FPB目标指向角度), Ycom(k)为系统控制器输出值, 受控对象为FPB的音圈电机所驱动的反射镜, Yout(k)为反射镜实际指向角度, r(k)为角度测量机构的输出值, kp, ki及kd分别为PID调节器中比例、积分及微分项的系数; 前馈补偿部分主要由微分项及比例项组成, kFF, i为前馈部分微分通道系数, kFF, p为前馈部分比例通道系数。当u(k)发生变化时, 前馈算法根据期望值计算出补偿值uFF(k), 进而对受控对象开环控制。同时PID算法根据u(k)与Yout(k)产生的偏差e(k)计算输出值Ycom(k), 从而实现闭环控制; 在受控对象向期望值运动过程中不断检测是否超出设定阈值范围, 如果超出该阈值范围, 则调整PID控制器的积分项, 防止积分饱和。整个复合PID控制器可由下式表示:
式中, Vi为PID算法积分项输出值, 离散计算公式为:
复合PID控制器流程图如图 3所示。
由上述图 3中流程可知, 前馈复合PID控制器所增加的前馈环节及防积分饱和项的计算过程无需迭代等计算量较大的过程, 因此其在计算能力受限平台上运行的实时性可得到有效保证。
-
精密光束指向系统的测试环境如图 4所示。该系统采用音圈电机(voice coil actuator, VCA)作为执行机构, 柔性铰链为镜面枢转元件。每轴采用两只电机推挽式配置以提高出力, 通过内部2维角度传感器反馈镜面实时转角, 并通过系统内部闭环控制, 完成镜面的高速精密指向控制。在本系统中, 系统主控芯片为TI公司TMS320F2812P, 降频至100MHz运行。x轴及y轴的复合PID控制器输出值分别通过14bit D/A数模转换器转为两路模拟电压信号, 并经电流放大后, 驱动音圈电机实现位置闭环控制。
实验中通过分别对该系统使用传统PID控制器及复合PID控制器时的阶跃响应及稳定指向进行测试, 从而在相同条件下, 对两种控制器的性能进行对比分析。由于系统运动部分为中心对称结构, 因此只对水平轴方向进行测试, 镜面偏转角度由自研非接触式角度传感器测量, 其分辨率为0.05″, 重复定位精度不大于0.5″, 采样频率为10kHz, 并在气浮光学平台上通过自准直仪进行校准。自准直仪型号为Acobeam AC300, 测角范围为±1200″, 分辨率为0.03″, 可满足对内部角度传感器校准的需求。角度采样值存储于主控芯片的内部存储空间, 采样深度为2048点。当存储空间满时, 通过程序中设置的断点停止采集, 并通过JTAG仿真器读取并存储为CSV文件, 通过Excel进行显示, 从而对FBP系统的特性进行比较测试。
-
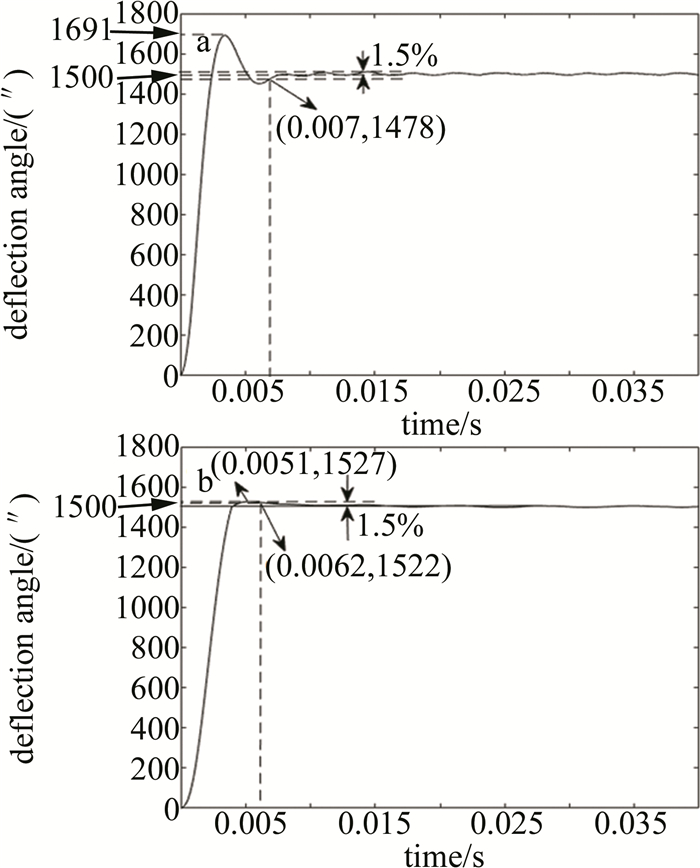
分别对使用传统PID控制器和复合PID控制器的精密光束指向系统输入1500″的阶跃信号, 以测试两者的瞬态性能。系统内部测角系统输出的阶跃响应分别如图 5a及图 5b所示。
将图 5中两种控制算法测试的系统阶跃响应数据中上升时间、最大超调量、允许误差带宽宽度以及系统的调整时间数据整理为表 1, 其中调节时间为系统超调量小于目标设定值的1.5%时所需时间。
transient
performancetraditional
PID controllercomposite
PID controllerratio rising time 1.6ms 2.2ms 138% overshoot 12.7% 1.8% 14% setup time 7ms 6.2ms 89% Table 1. Parameters of step-response performance by using traditional & composite PID controller
由表 1可知, 与采用传统PID控制器的系统相比, 使用复合PID控制器的系统的上升时间较长, 但其调整时间仅为前者的89%, 且超调量仅为前者的14%, 因此具有更好瞬态响应性能及更小的超调量, 从而解决了超调量与瞬态响应之间的矛盾。
-
向精密光束指向系统输入幅值为400″的阶跃信号, 对系统达到目标值后稳定情况进行测试, 测试结果如图 6所示。
图 6为系统反射镜偏转角度随采样点数变化曲线, 采样频率为10kHz。图 6a为采样复合PID控制器时的结果, 图 6b为采用传统PID控制器时的结果, 将两图中的数据整理为表 2。由表 2中可以看出, 与采用传统PID控制器的系统相比, 采用复合PID控制器的系统波动的峰峰值及稳态误差分别将为原系统的71.1%及73.3%, 从而可证明复合PID控制器的稳态性能优于传统PID控制器。
steady
performancetraditional PID
controller/(″)composite PID
controller/(″)ratio/% steady
state errorpeak-peak value 4.5 3.2 71.1 root mean square 0.75 0.55 73.3 Table 2. Parameters of steady performance by using traditional & composite PID controller
3.1. 瞬态性能测试
3.2. 稳态性能测试
-
研究分析了前馈补偿PID控制器原理, 并设计了基于收前馈补偿、抗积分饱和及传统PID控制器的复合PID控制器, 并将其应用于精密光束指向系统。实验结果表明, 在一定误差带宽度内, 复合PID算法使系统调整时间缩短了约11.4%, 最大超调量从12.7%降至1.8%, 在一定程度上解决了计算能力受限制的FPB系统中快速性与超调量的矛盾, 提高了系统的稳定性。从而可以广泛用于计算能力受使用环境限制的高速、精密运动伺服控制系统中。

 Map
Map









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: