HTML
-
周期性纳米结构滤光片对入射光的吸收率较小,其中心光谱位置、带宽等性能参量均可由结构参量进行调节,且易于集成,已成为彩色滤光片重要的研究和应用方向之一[1]。研究表明,当光栅周期远小于入射光波长时,只产生0级衍射光波,而其它较高级次的衍射光均为倏逝波,这类光栅称为亚波长光栅。通过调整亚波长光栅的取向、周期、深度等,对光选择性透射(反射/吸收),在光显示、光伏、光传感、光检测和无油墨印刷等领域的应用引起了广泛关注[2]。如果在液晶显示屏(liquid crystal display,LCD)中采用纳米光栅结构滤光片替代颜料型彩色滤光片,应满足以下要求:光能利用率高,透射带宽适中,旁带透射率低。中国专利“混合型偏振片及其制造方法和具有其的显示装置”中提出了一种埋入式单层金属光栅彩色滤光片[3],该彩色滤光片由位于基底上多个区域的不同周期、不同占空比、不同高度的金属光栅组成。
随着纳米加工技术的发展,导模共振滤光片以其设计结构简单、衍射效率高、半峰全宽(带宽)窄等优点引起了越来越多的关注。但大部分研究都是基于介质光栅的导模共振特性得到反射滤光片,基于表面等离子体效应的金属光栅的研究较少[3-5]。当光入射到金属光栅表面时,由于光子与金属表面自由电子的电荷密度波耦合成表面等离子体(surface plasmons,SP)在特定的光波长内表现出透射增强现象,这种现象称为表面等离子体效应。
目前,想要得到特定波长的滤光片,设计光栅结构,大多采用严格耦合波分析、模式法和时域有限差分等方法数值分析光栅周期、占空比、厚度等参量变化对透射谱线的影响,进而得到参量的优化范围[6]。本文中提出利用粒子群优化(particle swarm optimization, PSO)算法与严格耦合波分析(rigorous coupled wave analysis, RCWA)方法结合,在给定滤光波长要求的情况下,逆优化结构参量。粒子群优化是一种由一群鸟类和昆虫群的社会行为启发的进化计算技术。最初由KENNEDY和EBERHART提出,近年来主要应用于电磁场优化问题[7-8]。由于在各种问题中实现方便并且具有强大的优化能力,PSO算法越来越引起研究人员的注意。
本文中把光栅结构的参量作为优化的粒子,在一定范围内不断改变粒子的速度和位置,设定目标函数计算适应值F,对每组优化粒子进行评估,最终找到全局最优解。
-
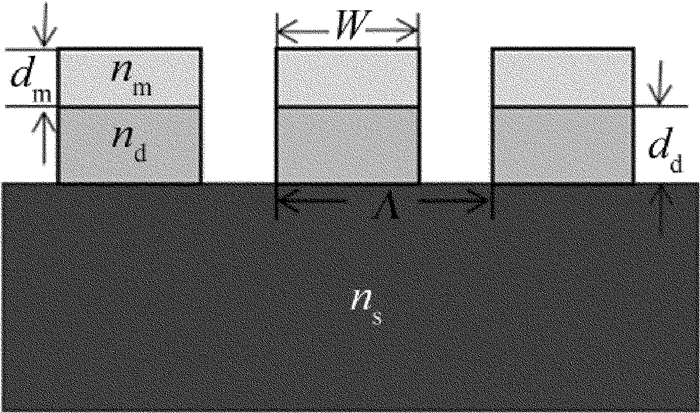
本文中研究一种基底-高折射率光栅-金属光栅的透射式滤光片结构,如图 1所示。金属光栅层材料为Al,折射率为nm,色散曲线依照Drude模型[9-11]。高折射率介质光栅层折射率nd=2.4,基底层折射率ns=1.5,Λ代表光栅的周期,光栅的宽度W=Λf,f为光栅的占空比,金属光栅层的厚度为dm,介质光栅的厚度为dd。当TM光从光栅表面垂直入射,金属表面发生等离子体共振。在金属和基底之间增加高折射率介质光栅层,满足波导共振激发条件,发生导模共振。由于这两种效应的共同作用,在特定波长发生透射增强。
2013年,ZHOU[2]提出当结构中的金属光栅厚度dm=0.06μm,介质光栅厚度dd=0.08μm,占空比f=0.75,周期Λ=0.4μm时,光谱峰值位置波长为0.65μm,透射效率为67%。为了提高光栅结构滤光片对波长为0.65μm红光的透射效率,缩小带宽,本文中提出利用PSO算法,逆优化结构参量。
在PSO中,群体的每个粒子被认为是N维搜索空间中的一个无质量的点,粒子仅具有两个属性:位置X和速度v,位置代表粒子移动的方向,速度代表粒子移动的快慢。每个粒子在搜索空间中寻找最优解,将其记为当前个体极值Pm,并将个体极值与整个粒子群里的其他粒子共享,找到最优的那个个体极值作为整个粒子群的当前全局最优解G,粒子群中的所有粒子根据自己找到的当前个体极值Pm和整个粒子群共享的当前全局最优解G来调整自己的速度和位置,直到输出全局最优解[12-14]。速度和位置的迭代公式为:
式中,ω是惯性权重,设定为从0.9~0.4递减,c1和c2设为1.49,Δt为时间步长,设为1,参量设置参见参考文献[15],rand( )为MATLAB自带函数,返回一个0~1之间的随机数,当前个体极值Pm={p1m, p2m, …, pnm},n=20, G=Pm,Pm和G迭代规则为:如果F(Xm, k+1)比F(Pm)小,则Pm由Xm, k+1取代。如果F(Pm)比F(G)小,则G被Pm取代。直到迭代结束。
对于通过PSO设计的金属光栅滤光片,本文中选择透射波长0.65μm的红光,选择4个参量作为优化参量:光栅厚度dm,介质层厚度dd,光栅周期Λ和占空比f。因此,粒子群数组为X={Λ,dm,dd,f}。设定目标函数,求适应值F公式如下[16]:
式中,Rt是不同波长入射光期望达到的透射效率,为了实现红光透射效率高、旁带低的要求,这里设定波长为0.65μm的透射效率达到最大值,此时最大值为1,带宽控制在小于50nm,设定波长为0.625μm和0.675μm时透射效率为0.3,其它波长对应透射效率设为0, 以减小旁带。Rd是把PSO中的优化参量代入RCWA程序计算所得到的透射效率,M是所取波长点的数量。粒子的F为两者的方差,反映了优化的程度,F越小,Rt越接近Rd,就越符合优化的结果。
-
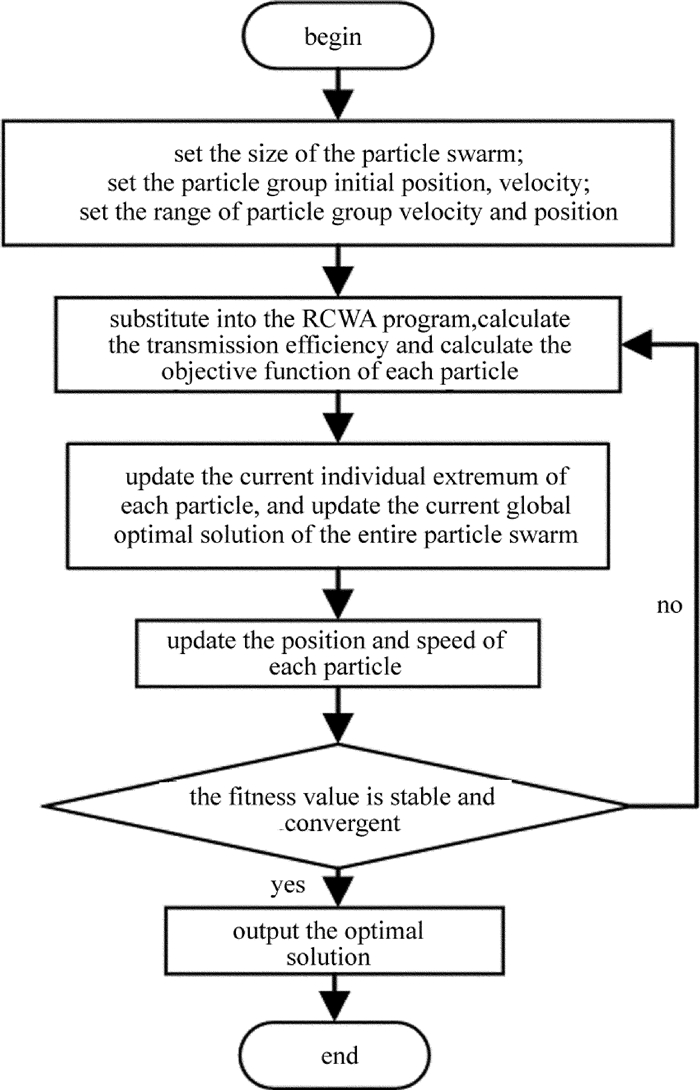
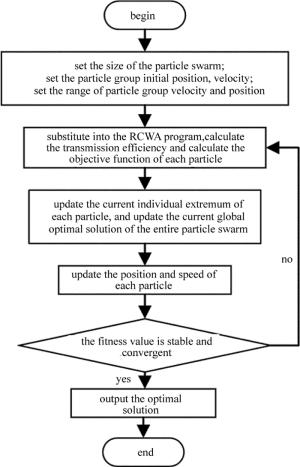
在MATLAB中进行仿真,仿真流程见图 2。在PSO程序模块中,首先分配粒子群中待定参量的初始数量,仿真过程中设定为20。参量的范围为:0μm < Λ < 0.650μm; 0μm < dm, dd < 0.500μm; 0 < f0.99;在范围内随机产生粒子的初始速度和位置。在RCWA程序中对图 1结构建模,设定基底、介质和金属材料,把PSO中随机产生的20组参量记为当前的个体极值,并分别代入到RCWA程序计算各组参量对应结构对各波长光的透射效率,根据(3)式,把RCWA程序获得的透射效率与设定曲线的透射效率代入到计算适应值的程序中, 得到这20组随机参量的适应值,把适应值最小的一组参量记为当前的全局最优解。根据迭代(1)式和(2)式,更新结构参量,重新代入RCWA程序,并计算适应值,比较每组参量迭代后的适应值与当前的个体极值,更新个体极值和全局最优解。重复以上流程,这里设定重复执行6000次,迭代次数足够多以确保适应值稳定且收敛[17-19]。
-
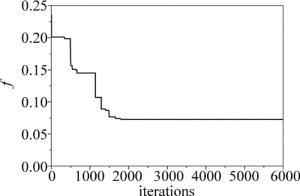
针对透射波长0.65μm的红光滤光片,图 3为PSO适应值随迭代次数变化的曲线。得到优化参量为:Λ=0.300μm,dm=0.035μm,dd=0.400μm,f=0.77,根据得到的最优参量模拟其对应结构透射效率随波长的变化曲线Rd(λ)与设定的透射效率曲线Rt(λ)的比较, 如图 4所示。设置虚线为目标曲线,实线为PSO优化结构的仿真曲线,点线为参考文献中ZHOU提出的结构透射光谱。
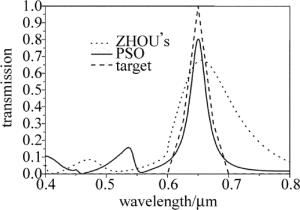
Figure 4. Relationship between transmission spectra of grating structure[2], the optimal structure and the target and wavelength
根据PSO算法得出的适应值随迭代次数变化图,以及最优结构透射效率随波长变化曲线与设定曲线对比的图形分析可知,迭代过程中适应值逐渐收敛,大约在2000次后趋于稳定,迭代6000次后得到适应值仅为0.0728,优化了结构参量,优化参量对应的光栅结构对红光透射率达到了80.27%,旁带效率控制在15%以内,半峰全宽(full width at half maximum,FWHM)仅为30nm。与ZHOU提出的结构透射光谱对比可知,此优化结构提高了透射效率,缩小了带宽。
在最优参量的基础上,通过改变单一参量,得到周期Λ、占空比f、金属光栅高度dm和介质光栅高度dd变化对透射效率的影响。图 5a中为当f=0.77,dm=0.035μm,dd=0.400μm,周期Λ分别为0.280μm, 0.290μm, 0.300μm, 0.310μm, 0.320μm时光栅结构对不同波长光的透射效率曲线。图 5b~图 5d中为固定其它参量,分别改变f, dm,dd时透射效率随波长变化的曲线。

Figure 5. Relationship between transmission and wavelength for different grating structure parameters
由分析可知,图 5a中, 当固定其它参量改变周期Λ时,随着Λ的变大,曲线红移,透射效率减小,周期小于最优值时,旁带大于20%,不能应用于整个可见光波段,周期大于最优值时,透射效率下降明显。图 5b中,当固定其它参量改变金属光栅厚度dm时,同样出现厚度小于最优值时,旁带超过20%,大于最优值时,透射效率显著下降。图 5c中,随着介质光栅厚度dd的增大,旁带透射效率也增大,厚度小于最优值时效率较低。图 5d中,随着占空比f的增大,曲线红移,在取最优值时旁带效率和透射效率与取其它值相比更优。因此,由PSO算法得出的最优结构实现了特定波长光的高效率透射。
-
将粒子群优化(PSO)算法应用到求解高效率透射光栅结构的结构参量上,利用MATLAB进行仿真,通过设定目标函数控制透射效率、旁带效率和带宽,不断迭代,比较适应值,使得仿真曲线与设定曲线的差值最小,实现了对光栅周期、占空比、光栅厚度、介质厚度的优化,优化结构对应的透射效率曲线在波长为0.65μm时达到最大,旁带效率小于15%,半峰全宽仅为30nm。在得到优化参量的基础上,分析了改变各个参量对透射效率的影响。研究表明,该亚波长金属-介质光栅滤光片结构实现了对波长为0.65μm红光的高效率透射。

 Map
Map



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: