HTML
-
采用光学方法进行气体体积分数检测具有速度快、精度高、非接触等优点[1-2]。基于这些优点,目前可调谐半导体激光吸收光谱(tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy,TDLAS)检测技术在发动机尾焰燃烧诊断[3-6]、痕量气体体积分数检测[7]、有毒有害气体遥测[8]等方面已经开展了大量研究和应用。有毒有害气体的来源通常是化工厂、化工仓库事故过程中形成的有毒有害气体云团。云团内部的有毒有害气体体积分数分布是确定救援方案的重要参考,TDLAS检测技术和计算机断层重建(computed tomography,CT)技术结合为气体体积分数分布远程确定提供了一个研究方向。
目前在气体检测领域,TDLAS检测一般采用波长调制或二次谐波进行检测。利用可调谐二极管输出波长在一定范围内可调的特点,能够同时分析多种污染物质,包括甲烷、一氧化碳、二氧化碳、一氧化氮、氨气等有毒有害气体。浙江大学JIANG等人[9]对基于TDLAS技术的望远镜收发系统的设计原理进行了研究,通过测量吸收池内甲烷标准气进行标定,并在单光程40m的遥测距离下验证了该系统的良好时间响应性。美国克莱蒙森大学MA等人在2008年提出了高光谱断层重建(hyper-spectral tomography, HT)技术[10],采用法布里-珀罗型光纤滤波激光器(fiber Fabry-Perot tunable filter laser, FFP-TFL),布置6条瞄准线(line of sight, LOS)测量路径并选择合适的吸收峰位测量了平面火焰炉的温度分布和H2O体积分数场,测量结果与相干反斯托克斯-喇曼光谱(coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectrum, CARS)的测量结果吻合良好。2011年, 该小组对HT方法进行了更深入的研究,采用15×15的分布式测量,将TDLAS系统安装在燃烧室出口处,获得温度、压力和水蒸气体积分数及这些变量的空间2维分布信息[11]。LIU等人[12]在对燃烧过程的温度进行检测的同时,也对产生的气体体积分数进行了实时测量。采用基于调制光谱的分频多路技术,对多台激光器采用不同频率的正弦电流信号进行调制,最终获得多组分的体积分数信息。天津大学的LI[13]利用TDLAS非接触测量的优点,将TDLAS双线测温技术用于高速燃烧流场的测量,选取1391.67cm-1和1468.89cm-1两条水蒸气的谱线,基于两台激光器建立了时分复用的测量系统,发展了一种基于TDLAS正交路径的2维燃烧场温度重建算法,研究了不同LOS测量路径数对单峰温度场和非对称双峰温度场的2维重建结果的影响,最后建立并验证了快速温度宽谱调谐多谱线测温体系。装备学院的SONG等人[14]采用非规则光线布局,提出了一种非规则光线分布优化原则,基于代数重建算法(algebraic reconstruction algorithm, ART)进行温度场2维分布重建。研究了发射端数目对重建结果的影响,通过实验验证得出了与仿真结果相吻合的结论。合肥工业大学的CHENG等人[15]将迭代重建算法用于不完全投影数据的重建工作中,针对光学遥感技术获取数据通常不完整的特点,对代数重建算法、乘型代数重建算法、联合代数重建算法、改进的联合代数重建算法等算法进行了改进,实验结果表明,改进算法在抗噪性方面有极大改善。中国科学院安徽光学精密机械研究所的XIA[16]等人使用改进的ART代数重建算法,对TDLAS检测结果进行了断层重建,获取了平面火焰炉燃烧产生水汽的2维分布重建结果。
痕量气体检测和燃烧诊断领域国内外已有大量研究,但对于有害气体的体积分数场分布测量研究较少,TDLAS技术本身的高分辨率特点决定了通常只需更换激光器即可完成不同气体的检测任务,因此将TDLAS检测技术用于有毒有害气体检测领域是完全可行的。本文中以常见的有害气体甲烷为研究目标,采用TDLAS技术进行非接触式体积分数测量,结合CT技术重建气体的体积分数场分布。实验中采用旋转台来实现对气体喷发区域的多角度扫描,获得24条光线数据,应用ART算法,来实现对6×6网格范围内甲烷气体的2维体积分数分布重建。
-
本文中主要采用TDLAS气体测量原理和代数重建算法来实现对甲烷扩散区域的2维体积分数分布重建。
-
TDLAS气体测量应用朗伯比尔定律[16]:
在单一跃迁前提下可以写作:
式中, It为透射光强(mW),I0为入射光强(mW);kν为光谱吸收系数(cm-1),由气体的静态压强p(Pa)、线强S(T)(cm-2·Pa-1)、线型函数φν和体积分数x确定;ν为入射光频率(cm-1),L为有效吸收光程(cm),φν为归一化的线型函数,其积分值为1。
对(2)式进行积分,进而忽略线型函数的影响,可以得到积分吸光度A和体积分数x之间的关系,即:
得到一个包含积分吸光度A、体积分数x、光程L的方程组。从而可以利用ART方法进行迭代计算。
-
ART代数重建算法是迭代重建法的一种形式,它的特点是:预设一初始图像x0,以x0为基础计算x1,进而根据x1计算x2,重复迭代至满足预设收敛条件,而后终止。每一次通过xk计算xk+1时,只需考虑一条光线产生的校正值Δxk,其所修正的数据网格也只包含这条光线通过的网格[17-20]。其本质上是通过一条条光线对所选初值的迭代修正,逐步令重建结果不断逼近实际值,在迭代修正过程中每一条光线并不总能起到正面的作用,在实验数据不够稳定的情况下,加入一些误差较大的光线将会放大误差,降低重建效果,对于重建算法中光线的选取是一个比较重要的环节,并且与实际测量的体积分数场分布及光线分布有着紧密的联系。
将(2)式改写为:
式中,A为实验数据处理后获得的积分吸光度向量,x为所求体积分数向量,而矩阵R则为投影系数矩阵。
采用ARTⅡ算法,则有:
式中,ik=k(modI)+1,k代表迭代次数,I是R的维数,λ为松弛因子,且取值在(0,2]之间,aik为积分吸光度A的分量,rik为投影系数矩阵R的分量,经过k次迭代满足截止条件时的xk即为重建结果。算法流程图如图 1所示。
1.1. TDLAS测量原理
1.2. 代数重建算法
-
本实验中采用如图 5所示装置。将用于模拟甲烷泄漏的平面炉放置在旋转台的中心,使用电磁流量计控制气流速度,在旋转台上正交方向布置两组光线准直器及探测器,每组6对,通过旋转至0°, 45°, 90°, 135°分别采样,共获取24路信号,激光器发出的光经由分束器连接到各个准直头,其中一路用于同步定标。实验设计在平面炉的中心点右上放置透光的石英柱,对比是否放置石英柱的重建结果来与仿真实验相互验证。
实验中使用Nanoplus公司的分布式反馈激光器(distributed feedback laser,DFB),其中心波长覆盖到甲烷吸收峰位1653.72nm,在常温下吸收强度良好。对采集到的信号进行处理,计算出,经过查表获取常温下的线强值为1.097×10-8cm-2·Pa-1,压强p=1.01×105Pa,可以计算出的值,然后将其作为迭代信息进行迭代重建。
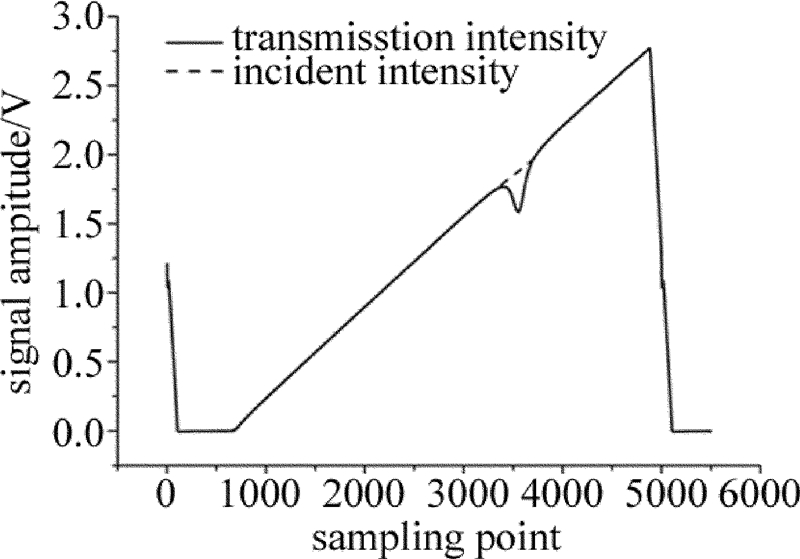
TDLAS信号检测采用直接测量法,获取信号如图 6所示。选取信号差异区域(长约500个点)前后各1000个点,利用干涉定标信号确定横坐标,然后计算积分吸光度A。
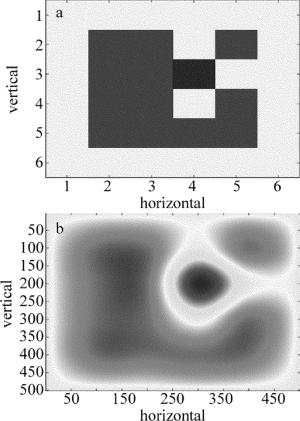
重建结果如表 1和图 7所示。表 1中上下两部分的6×6数据表格分别对应图 7a、图 7b各网格体积分数值。
volume fraction of methane 0 0.0002613 0.002157 0 0.003408 0 volume fraction distribution of Fig. 7a 1.199×10-6 0.01037 0 0.003102 1.638×10-6 0 0.005740 0 0.01137 0.0006311 0 0 1.382×10-6 0.0009636 0.006911 0 0.0006864 0.002332 3.653×10-6 0.004569 0 0.002429 0.0001081 0.001578 0.005721 3.653×10-6 1.382×10-6 0 0.001555 0.0004072 volume fraction of methane 0.0002642 0.0002642 0.0002642 0.007122 0.01247 0.007085 volume fraction distribution of Fig. 7b 0.01339 0 0 0.006233 0.006762 0 0.003168 0.01182 0.01704 0.01841 0 0.004573 0.01162 0.01373 0.004707 0 0 0.005895 0.005415 3.391×10-5 0 0.0003252 0.008037 0 0 3.610×10-5 0.01378 9.827×10-5 0 0 从图 7中的重建结果可以看出,平面炉出气并不均匀。图 7a、图 7b中已用方框标注出石英柱摆放区域。从图 7b、图 7d可以看出,在放置石英柱之前,甲烷主要集中在中心区域附近。从图 7a、图 7c可以看出,放置石英柱挡住了右侧之后,重建结果显示出右侧出现空穴,并对周边甲烷体积分数产生了影响,降低了右侧区域整体体积分数,左侧区域体积分数变化不大,与实验前预测相吻合。实验中遇到的主要问题在于气流的不稳定性,通过大量的重复试验来获取平均数据并不能完全克服这一问题,需采取增加单次扫描光线数量和提高气体体积分数缓和误差的方法改进实验,在考虑成本的前提下提高测量的准确度和重复性。
-
基于可调谐半导体激光吸收光谱技术,通过快速旋转台获取不同角度下的光线信息,使用ART代数重建算法对存在空穴的体积分数场进行重建,使用单激光器达成了这一目标,通过仿真实验和实际测量相互验证,为之后对气体体积分数场的快速3维重建打下基础。单激光器分束配合旋转台的实验方式硬件成本较低,与之相对的实验误差及时间成本也较多激光器分束、固定位多角度同时测量方法更大,对于变化较快的气体体积分数场而言,应用固定位多角度测量方式改进实验装置,提高数据时效性。

 Map
Map










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: