HTML
-
激光微织构技术可优化接触表面的摩擦学特性,提高零部件性能并延长使用寿命,已在发动机气缸、刀具、机械密封、滑动轴承套等领域得到重视[1-4]。激光微织构的实现主要是利用了激光与材料的热化学反应,其中基体材料能否对激光热量进行有效的吸收至关重要。然而一般金属材料对激光有着很高的反射率,室温下钛合金对1.054μm波长的钕玻璃激光反射率达到90%以上[5-6], 因此,改善材料在激光微织构加工中的吸光性能对科研和经济都有很重要的意义。
经研究发现,在加工之前通过对金属表面涂覆相应的涂料能够有效提高材料表面对激光的吸收[7-9]。传统的吸光涂料有碳素墨汁、磷化剂等,但存在吸光率低、气味刺鼻和清理困难问题[10-11]。近年来,研究人员以复合型金属氧化物为骨料研制了新型吸光涂料[12-13],与传统涂料相比,不仅能有效地提高激光吸收率,而且环境友好、易清除。但目前研究的大多数涂料都是针对于激光热处理工艺[14],而对激光微织构加工用吸光涂料的研究报道极少。作者所在课题组尝试用黑漆、硅油和石英水玻璃3种表层涂料进行试验,发现涂料可以抑制重熔金属生成毛刺,改善表面加工质量,其中水玻璃涂料的效果最为显著[15]。鉴于此,本文中通过对比研究几种吸光涂料的单一涂层以及其复合涂层对激光加工形成微织构的凹坑体积和表面质量的影响,并对涂层的作用机制进行探讨,为激光微织构加工用吸光涂料的推广应用提供依据。
-
黄料又名“吸光涂料”,呈黄色,由苏州大学激光加工中心生产。黑漆是三和自动喷漆,黑色,由广东三和化工科技有限公司生产。水玻璃又名“硅酸钠”,透明液体,由青岛优索化学科技有限公司生产。磷酸锌呈白色,由济宁佰一化工有限公司生产。分散剂是白色粉末,型号EBS,由济南宇舜化工生产。酚醛树脂是黄色片状颗粒,由河北成丰树脂化工有限公司生产。
-
试样材料为GCr15轴承钢,经高温淬火与回火处理后试样表面硬度为60HRC~65HRC,抛光处理后粗糙度Ra=0.1μm,如图 1所示。采用W-71s型喷枪将涂料喷涂到试样表面,控制喷涂距离约为40cm,涂层厚度控制为0.1mm左右,并置于室温下自然风干,制备单一涂料涂层及复合涂料涂层,如图 2所示。
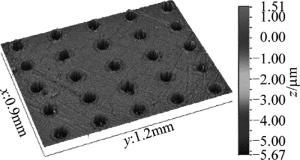
试样表面激光微织构加工采用本课题组自主研制的二极管抽运Nd:YAG激光加工机,如图 3所示。激光加工参量设置为激光重复频率为1600Hz,抽运电流为18A,脉冲重复次数3次,加工形成的表面微凹坑阵列如图 4所示。激光织构完成后,配合使用粒径为0.5μm的氧化铝抛光粉对试样表面进行轻微抛光处理。
-
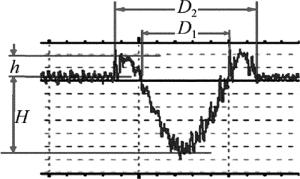
采用美国Veeco公司生产的WYKO-NT1100非接触光学轮廓仪对微织构凹坑内径D1、外径D2、深度H和熔渣高度h进行测量,结果如图 5所示。为了更好地表征涂料对激光加工的影响,可将凹坑等效为球冠体,其体积计算公式为V1=π(3HD12+4H3)/24,表面经过抛光处理后熔渣的尖角基本被抛平,因此可将其等效为正方体,体积计算公式为V2=πh(D22-D12)/4。对凹坑体积和熔渣体积进行计算并统计,结果如表 1所示。
number coating type inner diameter D1/μm outer diameter D2/μm height h/μm depth H/μm dimple volume V1/10-5mm3 slag volume V2/10-5mm3 C-0 none 79 114 0.70 7.0 1.73 0.37 C-1 black paint 67 100 0.40 6 0.83 0.17 C-2 water glass 86 110 0.36 6.0 1.75 0.13 C-3 yellow material 87 110 0.60 7.4 2.22 0.21 C-4 zinc phosphate 77.5 108 0.4 5.8 1.38 0.18 C-5 graphite 56 102.5 0.4 5.9 0.74 0.23 C-6 water glass+zinc phosphate 86 110 0.5 5.7 1.66 0.18 C-7 water glass+black paint 85.5 118.1 1 6.8 1.97 0.52 C-8 yellow material+water glass 88.3 108.2 0.7 8 2.48 0.21 C-9 yellow material+black paint 79 108.6 0.2 6.8 1.68 0.09 C-10 yellow material+zinc phosphate 84.5 117 0.8 6.8 1.92 0.41 Table 1. Parameters of dimple morphology
1.1. 涂层材料
1.2. 试样加工与制备
1.3. 实验设备及方法
-
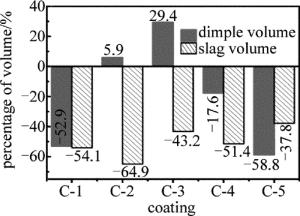
单一涂层表面凹坑蚀除体积和凹坑边缘熔渣体积变化率如图 6所示,其凹坑形貌如图 7所示。相比无涂层,C-1, C-4和C-5涂层表面均是凹坑边缘熔渣体积大幅减少,表面蚀除凹坑体积也大幅减少,表明试样表面质量有所提高,而激光微织构加工效率却受到削弱。其中C-5涂层(石墨)表面蚀除凹坑体积增加量最小为-58.8%,表面凹坑边缘熔渣体积减少量最大为37.8%, 与其它单一涂层相比,C-5涂层不仅表面微织构加工效率最低,加工质量也是最差。这是因为石墨材料的激光吸收效率过高,涂料表层吸收激光产生的大量热量来不及转移至基体材料,导致涂层被烧蚀并蒸发电离生成了对激光微织构加工起屏蔽作用的等离子体,故C-5涂层会严重阻碍微凹坑的形成,大大削弱了激光微织构加工效率。
相比无涂层,C-2涂层表面蚀除凹坑体积增加了5.9%,凹坑边缘熔渣体积减少了64.9%;C-3涂层表面蚀除凹坑体积增加了29.4%,凹坑边缘熔渣体积减少了43.2%。这表明C-2和C-3涂层不仅大幅提高了激光加工效率,而且显著改善了激光加工表面质量。这是因为C-2(水玻璃)与基体结合性能好,热传导率高,C-3(黄料)具有很强的吸光性能,所以当激光能量被基体表面的涂层所吸收并转化为热能后,基体表层均可以接收涂层传递来的大量能量,使得基体表层烧蚀形成的凹坑内径和深度变大,从而获得体积更大的微凹坑。同时凹坑边缘的涂层不仅可以抑止金属在重熔的过程中生成毛刺,还可以阻碍在激光烧蚀过程中飞溅出的残渣在基体表面的堆积,有效地控制了熔渣体积。实验表明,相比C-2涂层,C-3涂层可以更好地吸收能量并传递到基体。
-
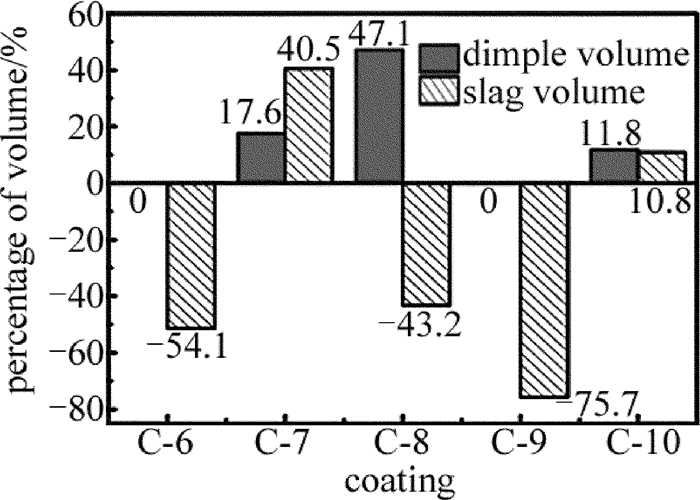
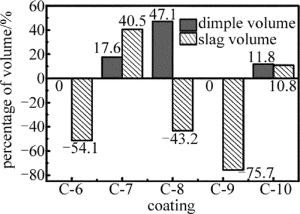
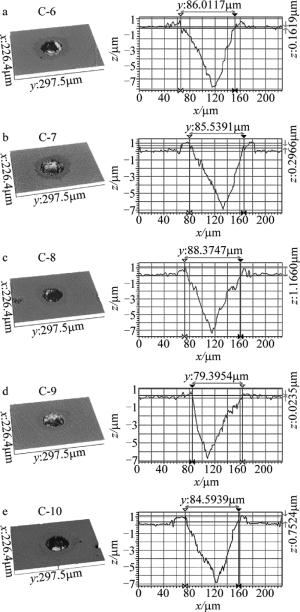
复合涂层表面凹坑蚀除体积和凹坑边缘熔渣体积变化率柱状图如图 8所示,其凹坑形貌如图 9所示。相比无涂层,C-7, C-8和C-10涂层表面凹坑蚀除体积分别增加了17.6%, 47.1%和11.8%。凹坑边缘熔渣体积分别增大40.5%, -43.2%和10.8%。这表明,虽然C-7, C-8和C-10涂层均能提高激光表面微织构加工效率,但C-7和C-10涂层会降低激光表面微织构的加工质量,而C-8涂层却能提高微织构加工质量。这是因为C-8涂层中的C-2材料良好的粘结性与C-3材料显著的吸光性表现出“协同”作用,不仅可以大幅提高激光表面微织构加工效率,还能显著提高激光表面微织构加工质量。在激光表面微织构加工质量方面,C-7涂层中的C-1材料(黑漆)主要成分是炭黑,其与C-2材料发生反应会产生某种结合界面,弱化了对熔渣堆积的阻隔作用,从而使激光表面微织构加工质量得到降低。
相比无涂层,C-6涂层表面凹坑边缘熔渣体积降低了51.4%,大幅改善了激光表面微织构加工质量,但是其表面凹坑蚀除体积并没有得到提高。这是因为C-6涂层是由C-2和C-4材料(磷酸锌)组成,而C-2材料主要成分是硅酸钠,遇到C-4材料(磷酸锌)发生反应并生成一些吸光性和导热性差的物质,削弱了复合材料对激光的吸收性能和对热能的传导性能,故激光表面微织构加工效率没能得到提高。但两者复合产生的结合面结构稳定,有效阻隔了飞溅落在凹坑周围的熔渣与基体的接触,使熔渣更容易脱落,激光表面微织构加工质量得到改善。
-
相比单一涂层C-1和C-2,复合涂层C-7表面蚀除凹坑体积分别增加70.5%和11.7%,而其表面凹坑边缘熔渣体积分别提高了94.6%和105.4%。表明复合涂层C-7相比单一涂层C-1和C-2可以更好地提高激光表面微织构加工效率,并且其效果高于单一涂层C-1和C-2之和。这是因为C-1材料吸光性能较好,但由于其粘结性能较差,影响了激光能量从涂层到基体的传送效率,而C-2具有较好的粘结性能,使得由C-1和C-2复合而成的C-7涂层同时拥有了良好的吸光性能和粘结性能。故复合涂层既能高效地吸收激光能量,又能有效地传送热量到达基体,产生了“1+1>2”的效果,使得蚀除基体的材料更多,激光表面微织构加工质量得到大幅度提高。但是在激光表面微织构加工质量方面,C-1和C-2结合生成的新界面在外力作用下容易受到破坏,激光加工时从凹坑中飞溅出来的熔渣更容易穿透涂层与基体重铸,并在凹坑周围形成堆积,故该复合涂层的加工质量与单一涂层相比出现降低。
相比单一涂层C-2和C-4,复合涂层C-6表面凹坑蚀除体积分别增加了-5.9%和17.6%,而其表面凹坑边缘熔渣体积分别提高了13.5%和0。表明复合涂层C-6相比单一涂层C-4能够显著提高激光表面微织构加工效率,相比单一涂层C-2却降低了激光表面微织构加工效率。这是因为复合涂层C-6中,C-2材料的粘结性能良好且能够将激光能量有效地传递到基体表层,而C-4材料的吸光性能较差,两种材料的作用相互“抵消”,使得其激光微织构加工效率没有得到明显的提升。在激光表面微织构加工质量方面,复合涂层C-6加工质量与单一涂层C-2和C-4相比并没有得到提高,但与无涂层相比,其表面微织构的加工质量仍然有显著的改善,这说明C-2和C-4的结合界面仍然可以大幅提高激光表面微织构加工质量。
相比单一涂层C-2和C-3,复合涂层C-8表面凹坑蚀除体积分别提高了41.2%和17.7%,而其表面凹坑边缘熔渣体积分别降低了21.7%和0%。表明C-8复合涂层相比单一涂层C-2和C-3可以更好地提高激光表面微织构加工效率,且其效果高于单一涂层C-2和C-3之和,而激光表面微织构加工质量不会受到影响。这是因为C-2具有良好的粘结性能,C-3又具有很强的吸光性能,使得由C-2材料和C-3材料复合产生“1+1>2”的效果,使得复合涂层既能大幅提高织构加工效率,同时也能明显改善织构加工质量。
2.1. 单一涂层激光微织构性能分析
2.2. 复合涂层激光微织构性能分析
2.3. 复合涂层与单一涂层的激光微织构性能对比分析
-
(1) 相比于无涂层试样,单一涂层水玻璃和黄料不仅可以大幅提高激光表面微织构加工效率,而且能够显著改善激光表面微织构加工质量。
(2) 在一定条件下,由于不同涂层材料的协同作用,复合涂层相比单一涂层具有更好的激光加工性能。其中,水玻璃与黄料复合性能最佳,与未经涂层的相比,凹坑蚀除体积增加了47.1%,凹坑边缘熔渣体积减少了43.2%。
(3) 复合吸光涂层能有效提高零件激光表面加工效率和改善加工质量,在激光微织构加工中具有良好的应用前景。

 Map
Map






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: